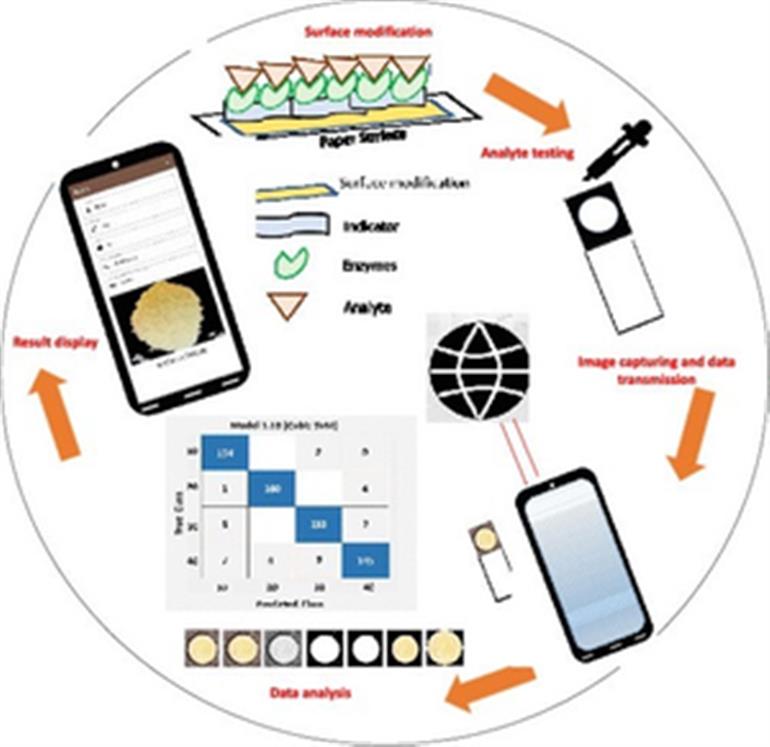
Jodhpur: Researchers on the Indian Institute of Know-how (IIT) Jodhpur have developed a brand new low-cost, paper-based analytical system that may be related to smartphones to offer on-spot detection of glucose ranges.
The system carries a lab-based functionalised biodegradable paper which adjustments color primarily based on the extent and quantity of glucose current.
When related to a smartphone, it gives fast, easy-to-access, and even personalised outcomes.
“This system can present on-the-spot glucose testing outcomes with out requiring technical or refined laboratory settings. Moreover, it’s designed to be cost-effective and biodegradable, with the present price at solely about Rs. 10 within the lab. The workforce hopes to additional make it even cheaper throughout mass manufacturing, at Rs 5,” stated the researchers in an announcement.
Whereas paper-based analytical gadgets have been in use earlier, they required particular gentle situations to work.
Nevertheless, the researchers employed machine studying to make the system suitable with all smartphones to work and transmit data seamlessly below almost all attainable gentle situations.
“Smartphones supply seamless integration with different applied sciences and platforms. The power to attach the smartphone-based spot detection framework to a bigger community or database can facilitate distant monitoring, knowledge storage, and sharing of outcomes. This connectivity might be essential for healthcare professionals or researchers,” stated Ankur Gupta, Affiliate Professor, Division of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Jodhpur, within the assertion.
The researchers famous that the know-how might be adaptable for the screening and diagnostic evaluation of uric acid, and different illnesses. The findings are printed within the journal ACS Publications.
“This research demonstrates that this developed system is provided for preliminary illness screening on the person finish. By incorporating machine studying strategies, the platform can present dependable and correct outcomes, thus paving the way in which for estimating the accuracy of the outcomes for improved preliminary healthcare screening and prognosis of any illness,” Ankur stated.